What is soil carbon?
C is the fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium and oxygen, and is the primary basis of life on Earth.
The ability of C to form many bonds allows it to form large complex molecules that attach to other elements that are essential to life, such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and sulphur (S). These bonds also trap energy as a source of fuel for microorganisms.
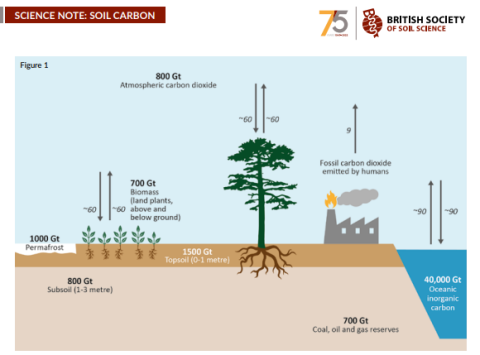
When plants, animals and microorganisms die and decompose, their remains form organic matter of which about half is C, and on land this combines with weathered minerals from rock (inorganic material) to form soil.
After the world’s oceans, soil is the world’s largest active C store, holding 80% of terrestrial C, which is almost three times the amount held in the world’s atmosphere.